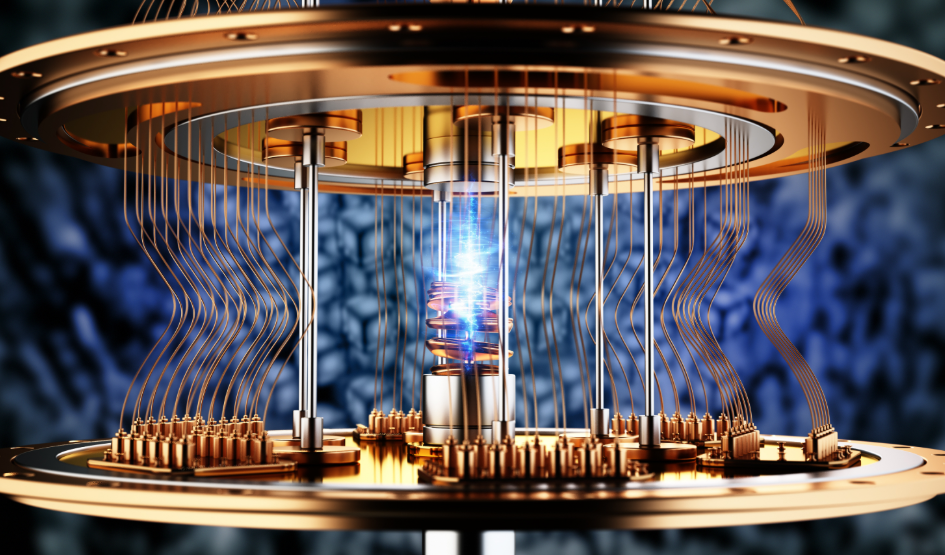
Quantum computers present several notable limitations that hinder their broader application. High error rates and quantum decoherence significantly affect qubit reliability, resulting in decreased computational fidelity. Furthermore, the inherently short coherence times of qubits limit the practical implementation of complex algorithms. Scalability remains a prominent challenge, complicating the transition to larger systems. These issues raise critical questions about the future utility of quantum computing in solving complex problems effectively.
Error Rates and Quantum Decoherence
Although quantum computers hold immense potential for computational advancements, they are significantly hindered by high error rates and the phenomenon of quantum decoherence.
Effective error correction techniques and robust noise mitigation strategies are essential to enhance qubit reliability. Without these advancements, the practicality of quantum computing remains limited, impeding its ability to fully realize its transformative potential in various fields.
See also: Introduction to Wearable Technology
Limited Qubit Coherence Times
How do limited qubit coherence times impact the performance of quantum computers?
The stability of qubits is essential for effective quantum operations. Short coherence durations lead to rapid loss of quantum information, impairing computational fidelity.
Consequently, algorithms that require prolonged qubit interactions become less viable. This limitation significantly restricts the potential of quantum systems to solve complex problems efficiently, undermining their practical applications.
Challenges in Scalability
As quantum computing technology advances, scalability emerges as a critical challenge that must be addressed to achieve practical implementation.
The limitations imposed by quantum architecture and hardware constraints hinder the ability to scale systems effectively.
These challenges necessitate innovative solutions to enhance qubit interconnectivity and error correction, ensuring that larger quantum systems can operate efficiently while maintaining coherence and reliability.
Specific Use Cases and Limitations
The exploration of quantum computing’s potential is often tempered by the recognition of its specific use cases and inherent limitations.
While quantum supremacy offers promise for tasks like cryptography and optimization, the efficiency of algorithms remains a critical challenge.
Current implementations struggle to outperform classical counterparts in many scenarios, highlighting the necessity for further advancements in both hardware and software to achieve practical applications.
Conclusion
In the realm of computing, quantum computers are akin to fragile glass sculptures—intricately designed yet vulnerable to the slightest disturbance. Their high error rates and fleeting coherence times resemble cracks that jeopardize their structural integrity, while scalability challenges loom like an expansive chasm, hindering their journey toward greater heights. Until innovation fortifies their foundations, these ethereal constructs remain unable to fully transcend classical paradigms, trapped in a delicate balance between potential and limitation.